🏠 50/30/20 Budget Rule: Smart Budgeting Strategy for Indian Households
Introduction
Managing money wisely is essential in today’s fast-paced life. The 50/30/20 budget rule offers a simple, flexible method to plan your finances. Whether you’re a salaried employee, freelancer, or homemaker, this budgeting strategy helps you track expenses and save efficiently.
What is the 50/30/20 Budget Rule?
The 50/30/20 budget rule is a money management method that divides your monthly income into three categories:
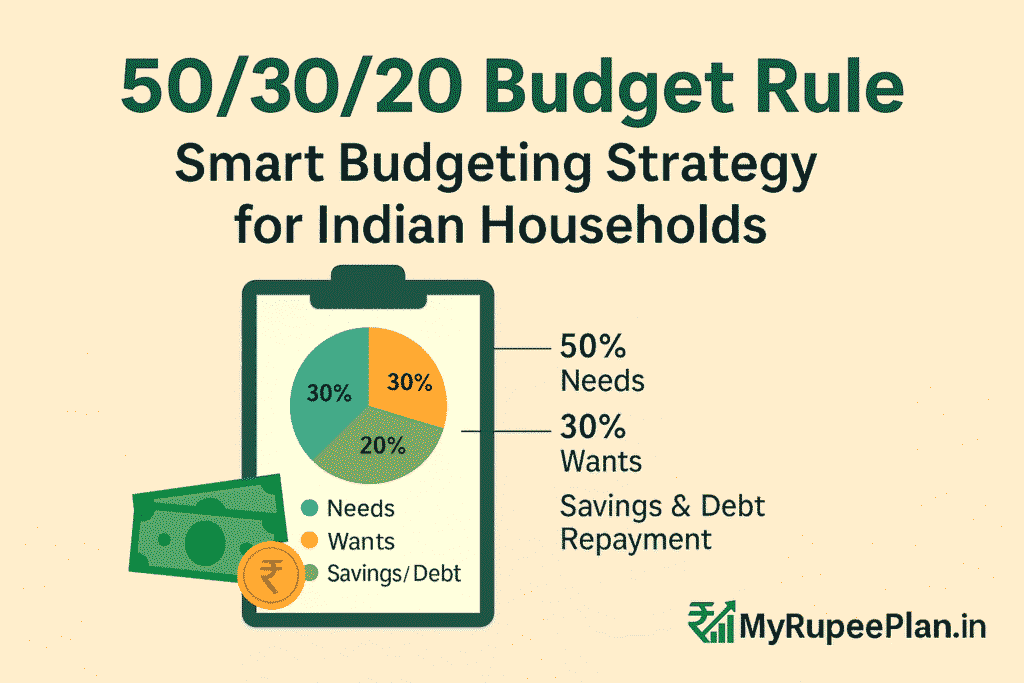
- 50% for Needs
- 30% for Wants
- 20% for Savings & Debt Repayment
This framework was popularized by U.S. Senator Elizabeth Warren in her book “All Your Worth: The Ultimate Lifetime Money Plan.”
How It Works in India
| Category | Percentage | Amount | Example Expenses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Needs | 50% | ₹25,000 | Rent, groceries, bills, transportation |
| Wants | 30% | ₹15,000 | Dining out, OTT, shopping, entertainment |
| Savings/Debt | 20% | ₹10,000 | SIPs, PPF, emergency fund, loan EMIs |
🔍 Breaking Down the Categories
✅ 50% – Needs
These are non-negotiable expenses. For most Indian families, this includes:
- House rent or EMI
- Utility bills
- School fees
- Groceries and daily essentials
- Basic transportation
✅ 30% – Wants
Wants are lifestyle choices—not necessary, but enjoyable:
- Dining at restaurants
- Netflix, Amazon Prime subscriptions
- Gym memberships
- Vacations, gadgets
✅ 20% – Savings & Debt
This portion secures your financial future. Include:
- SIPs and mutual fund investments
- Emergency fund
- Credit card/loan repayments
- Retirement plans like NPS, PPF
📊 Advantages of the 50/30/20 Rule
✅ Simplicity: Easy to understand and apply
✅ Flexibility: Adjust as per income changes
✅ Goal-Oriented: Encourages savings and debt control
✅ Improved Awareness: Tracks where your money goes
🤔 Is 50/30/20 Practical for Indian Households?
Yes, but with modifications based on income:
- Low-income earners: Needs may exceed 50%. Reduce wants to 20% and savings to 10%.
- High-income earners: Can increase savings up to 30–40%.
- Joint families: Consider total household income and shared expenses.
🧠 Pro Tips for Success
- Use budget-tracking apps like Walnut, Goodbudget, or Excel
- Review your budget monthly
- Automate savings through SIPs or RD
- Prioritize emergency fund over luxury spends
🧾 Example: ₹40,000 Monthly Income
| Category | % | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Needs | 50% | ₹20,000 |
| Wants | 30% | ₹12,000 |
| Savings/Debts | 20% | ₹8,000 |
Even ₹8,000/month saved leads to ₹96,000/year!
🧾 FAQs: 50/30/20 Budget Rule
1. What is the 50/30/20 budget rule?
It’s a budgeting rule where 50% of income goes to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings or debt.
2. Can Indians use the 50/30/20 rule?
Yes, it’s flexible and works well when adapted to Indian spending habits.
3. How do I calculate my 50/30/20 budget?
Multiply your monthly income by 0.5, 0.3, and 0.2 for needs, wants, and savings respectively.
4. What counts as a need or want?
Needs: rent, groceries, bills.
Wants: eating out, shopping, entertainment.
5. What if needs exceed 50%?
✅ Conclusion
The 50/30/20 budget rule offers a balanced and disciplined approach to money management. Whether you’re new to budgeting or looking to optimize your savings, this rule can be your roadmap to financial freedom.
